In this article, I am going to discuss the Static and Non-Static Members in C# with some examples. Please read our previous article before proceeding to this article where we discussed the Data Type in C# with examples. At the end of this article, you will be having a very good understanding of the following pointers.
- What are static and non-static members in C#?
- When do we need to use static and non-static members in C#?
- Static and Non-static variables in C#.
- What is the scope of Non-Static variables in C#?
- Static and Non-Static methods in C#.
- What is Static and Non-Static Constructor in C#?
- Understanding Static class in C#.
What are static and non-static members in C#?
The member of a class is divided into two categories
- Static members
- Non-static members
In simple word, we can define that, the members of a class which does not require an instance for initialization or execution are known as the static member. On the other hand, the members which require an instance of a class for both initialization and execution are known as non-static members.
Understanding the Static and Non-static variables in C#
Whenever we declare a variable by using the static modifier or when we declare a variable inside of any static block then those variables are considered as static variables whereas the rest of the other are considered as non-static variables.
If you want a variable to have the same value throughout all instances of a class then you need to declare that variable as a static variable. So, the static variables are going to hold the application level data which is going to be the same for all the objects. Have a look at the following example.

The static variable gets initialized immediately once the execution of the class starts whereas the non-static variables are initialized only after creating the object of the class and that is too for each time the object of the class is created.
A static variable gets initialized only once during the life cycle of a class whereas a non-static variable gets initialized either 0 or n number of times, depending on the number of objects created for that class.
If you want to access the static members of a class, then you need to access them using the class name whereas you need an instance of a class to access the non-static members.
Let us see an example for better understanding:
- namespace StaticNonStaticDemo
- {
- class Example
- {
- int x; // Non statuc variable
- static int y = 200; //Static Variable
- public Example(int x)
- {
- this.x = x;
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- //Accessing the static variable using class name
- //Before object creation
- Console.WriteLine("Static Variable Y = " + Example.y);
- //Creating object1
- Example obj1 = new Example(50);
- //Creating object2
- Example obj2 = new Example(100);
- Console.WriteLine($"object1 x = {obj1.x} object2 x = {obj2.x}");
- Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
OUTPUT:

What is the scope of Non-Static variables in C#?
The Non Static variables are created when the object is created and are destroyed when the object is destroyed. The object is destroyed when its reference variable is destroyed or initialized with null. So we can say that the scope of the object is the scope of its referenced variables.
Static and Non-Static methods in C#
If we declare a method using the static modifier then it is called as a static method else it is a non-static method. You cannot consume the non-static members directly within a static method. If you want to consume any non-static members with a static method then you need to create an object that and then through the object you can access the non-static members. On the other hand, you can directly consume the static members within a non-static method without any restriction.
Rules to follow while working with static and non-static members in c#:
- Non-static to static: Can be consumed only by using the object of that class.
- Static to static: Can be consumed directly or by using the class name.
- Static to non-static: Can be consumed directly or by using the class name.
- Non-static to non-static: Can be consumed directly or by using the “this” keyword.
Let us understand this with an example:
- namespace StaticNonStaticDemo
- {
- class Example
- {
- int x = 100;
- static int y = 200;
- static void Add()
- {
- //This is a static block
- //we can access non static members X with the help of Example object
- //We can access the static member directly or through class name
- Example obj = new Example();
- //Console.WriteLine(obj.x + Example.y);
- Console.WriteLine("Sum of 100 and 200 is :" + (obj.x + y));
- }
- void Mul()
- {
- //This is a non-static method
- //we can access static members directly or through class name
- //we can access the non-static members directly or through this keyword
- Console.WriteLine("Multiplication of 100 and 200 is :" + (this.x * Example.y));
- Console.WriteLine("Multiplication of 100 and 200 is :" + (x * y));
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- // Main method is a static method
- // ADD() method is a static method
- // Statid to Static
- // we can call the add method directly or through class name
- Example.Add();
- Add();
- // Mul() method is a non-static method
- // we can call the non-static method using object only from a static method
- // Static to non-static
- Example obj = new Example();
- obj.Mul();
- Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
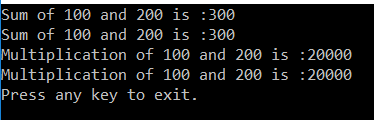
OUTPUT:
Understanding Static and Non-Static Constructor in C#:
If we create the constructor explicitly by the static modifier, then we call it a static constructor and the rest of the others are the non-static constructors.
The most important point that you need to remember is the static constructor is the fast block of code which gets executes under a class. No matter how many numbers of objects you created for the class the static constructor is executed only once. On the other hand, a non-static constructor gets executed only when we created the object of the class and that is too for each and every object of the class.
It is not possible to create a static constructor with parameters. This is because the static constructor is the first block of code which is going to execute under a class. And this static constructor called implicitly, even if parameterized there is no chance of sending the parameter values.
Let us understand this with an example:
- namespace StaticNonStaticDemo
- {
- class Example
- {
- static Example()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("static constructor is called");
- }
- public Example()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("non-static constructor is called");
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("Main method is executed");
- Example obj1 = new Example();
- Example obj2 = new Example();
- Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
OUTPUT:

Understanding the Static class in C#:
The class which is created by using the static modifier is called a static class. A static class can contain only static members in it. It is not possible to create an instance of a static class. This is because it contains only static members. And we know we can access the static members of a class by using the class name.
Let us understand this with an example.
- namespace StaticNonStaticDemo
- {
- public static class TemperatureConverter
- {
- public static double CelsiusToFahrenheit(string temperatureCelsius)
- {
- // Convert argument to double for calculations.
- double celsius = Double.Parse(temperatureCelsius);
- // Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- double fahrenheit = (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32;
- return fahrenheit;
- }
- public static double FahrenheitToCelsius(string temperatureFahrenheit)
- {
- // Convert argument to double for calculations.
- double fahrenheit = Double.Parse(temperatureFahrenheit);
- // Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius.
- double celsius = (fahrenheit - 32) * 5 / 9;
- return celsius;
- }
- }
- class TestTemperatureConverter
- {
- static void Main()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("Please select the convertor direction");
- Console.WriteLine("1. From Celsius to Fahrenheit.");
- Console.WriteLine("2. From Fahrenheit to Celsius.");
- Console.Write(":");
- string selection = Console.ReadLine();
- double F, C = 0;
- switch (selection)
- {
- case "1":
- Console.Write("Please enter the Celsius temperature: ");
- F = TemperatureConverter.CelsiusToFahrenheit(Console.ReadLine());
- Console.WriteLine("Temperature in Fahrenheit: {0:F2}", F);
- break;
- case "2":
- Console.Write("Please enter the Fahrenheit temperature: ");
- C = TemperatureConverter.FahrenheitToCelsius(Console.ReadLine());
- Console.WriteLine("Temperature in Celsius: {0:F2}", C);
- break;
- default:
- Console.WriteLine("Please select a convertor.");
- break;
- }
- // Keep the console window open in debug mode.
- Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- }
- }
OUTPUT:

In the next article, I am going to discuss const and read-only variables in C# with examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain the static and non-static members in C# with some examples. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.





0 comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.