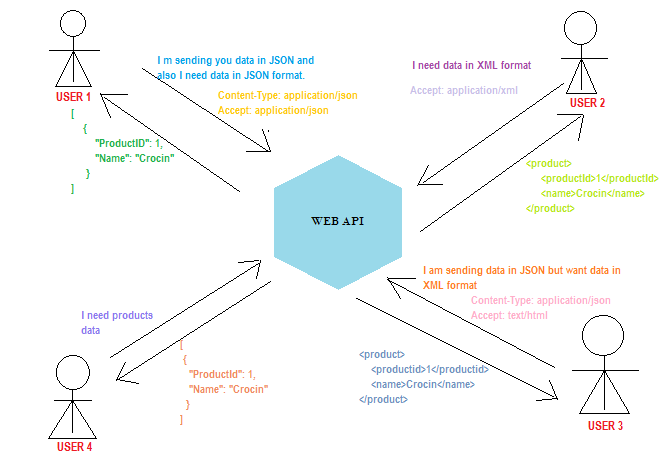
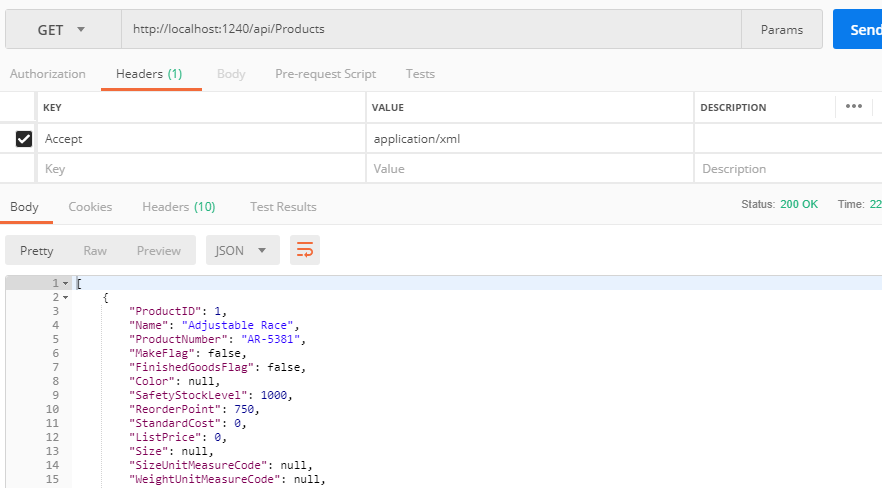
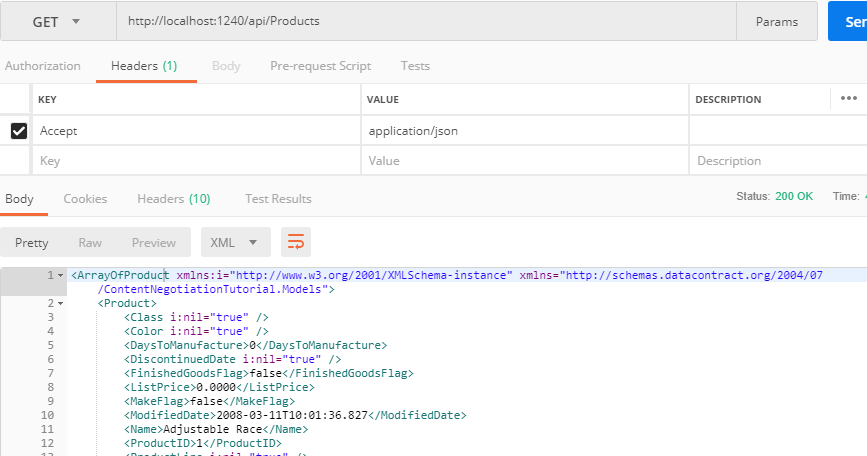
Ionic 6 Angular Geolocation and Geocoder tutorial; This is a step by step tutorial on how to use Cordova Geolocation and Geocoder plugin in an Ionic app to get the current user device position, get current user address.
We will look at how to add target platforms such as iOS, Android or Windows and create the build in Ionic for various devices.
Ionic 6 Angular Get Geolocation Example
- Step 1: Prerequisite
- Step 2: Create New Ionic Angular Project
- Step 3: Install & Configure Cordova Geolocation and Geocoder Plugins
- Step 4: Get Current Location Latitude and Longitude
- Step 5: Get Current Address
- Step 6: Start Ionic App
Prerequisite
We must have the latest version of Node js installed on our device. If you are not having then follow this tutorial on: How to Download and Install Node.js and npm
Create New Ionic / Angular Project
Use the command to install Cordova globally on your machine.
By using the following command, you can check the Ionic CLI version running on your machine.
Use below command to update Ionic and Cordova.
Let’s start installing a brand new Ionic Angular app with the help of Ionic CLI, run the following command in your terminal.
Get inside the project folder.
Start the app in the browser.
How to Install & Configure Cordova Geolocation, Geocoder and Ionic Native Plugins
In this step, we will first install then configure Cordova Geolocation, Geocoder and Ionic native plugins in an Ionic app.
Geolocation
The cordova-plugin-geolocation plugin API is based on the W3C Geolocation API Specification and helps to get the location (latitude and longitude) data.
This plugin provides information about the device’s location, such as latitude and longitude. Common sources of location information include Global Positioning System (GPS) and location inferred from network signals such as IP address, RFID, WiFi and Bluetooth MAC addresses, and GSM/CDMA cell IDs.
Install @ionic-native/geolocation via npm using the below command.
This geo location plugin provides device data such as device location, latitude and longitude. Common sources of location information include Global Positioning System (GPS) and location inferred from network signals such as IP address, RFID, WiFi and Bluetooth MAC addresses, and GSM/CDMA cell IDs.
It supports following platforms:
- iOS
- Android
- Windows
- Browser
- Amazon Fire OS
Add given below configuration to your configuration.xml file for iOS support.
Native Geocoder
The native geocoder plugin helps us to get the address for given coordinates and also does forward and reverse geocoding for iOS and Android platforms.
Import Plugins in Main AppModule
Add the above plugins in the main Ionic app module file, open app.module.ts file, and import and add plugins in an import array.
Get Current User’s Device Location Latitude and Longitude using Geolocation and Native Geocoder Plugin
Apps like Whatsapp, Uber, Ola, and many more depending on the user’s location, and without location, we can’t imagine modern days web and mobile applications. Almost every application uses the location service to offer excellent services to its users.
Finding a geo location with Cordova Geolocation is very easy, and We are going to get the current lat long of the user’s device.
In this step, I am going to describe how to locate the user’s device position, open home.pge.ts file and add the given code in it.
To get the geographical position of a user, we imported the Geolocation API at the top, then injected in the constructor and accessed the getCurrentPosition() method to get the user’s position.
The getCurrentPosition() method returns geolocation data which contains a timestamp, GeoLocation coordinates such as latitude, longitude, altitude, accuracy, alititudeAccuracy, heading and speed.
The getCurrentPosition() function takes 3 parameters, success, error and options. In the options we specify timeout, enableHighAccuracy and maximumAge.
Add the following code in home.page.html file.

Getting Current Address
To get the current address of the location. We need to import the following services at the header part of the Ionic TypeScript template.
Open the home.page.ts file then add the following code.
We defined address variable, then injected the NativeGeocoder API in the constructor.
The getAddress() method takes lat and long parameter, inside the function the reverseGeocode API provides reverseGeocode method that takes lat, long and nativeGeocoderOptions parameters and returns the address array. That raw address data is being filtered by pretifyAddress() method and returning comma separated address.
Start Ionic App in Device
We will learn how to add target platforms for iOS, Android and Windows to test our app.
Use the following commands to build your Ionic app for various platforms:
Start the app in the device.
Conclusion
Finally, Ionic Cordova Geolocation and Geocoder plugins tutorial has been over. In this tutorial we have learned how to:
- Set up a basic Ionic app from scratch.
- Install and configure Cordova Geolocation and Geocoder Plugins in Ionic app.
- Locate Current Location Latitude and Longitude.
- Get Current User Address.
- Add Target Platforms.
- Build Ionic App.