Introduction
In this article, we will be creating a personal expense manager using Asp.NET Core 2.1 and Entity Framework core Code first approach. An expense manager tracks your daily expenses and provides comparative charts to show expense summary. Since we are using modal dialog to handle user inputs and to show monthly and weekly expense summary chart using Highcharts. Hence this application will be a Single Page Application (SPA) .
We will be using Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2017 for our demo.
Let us look at the final application.
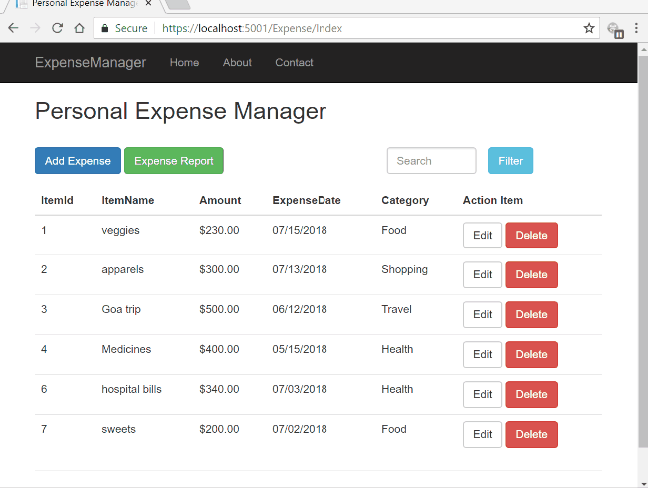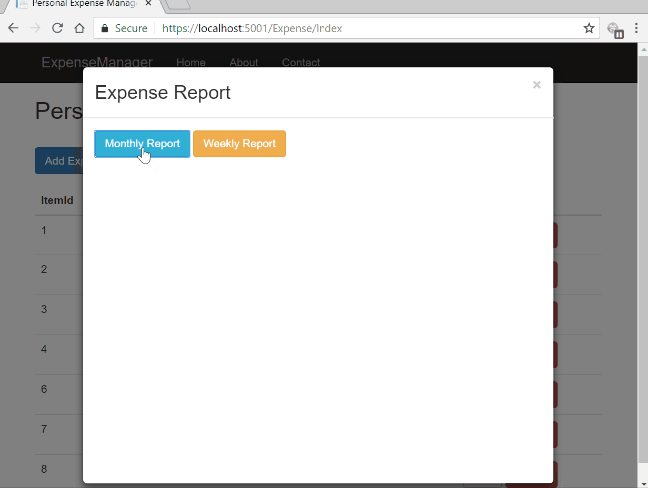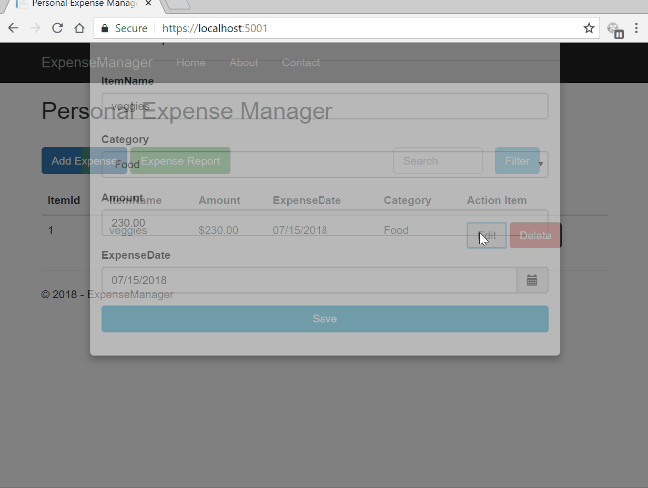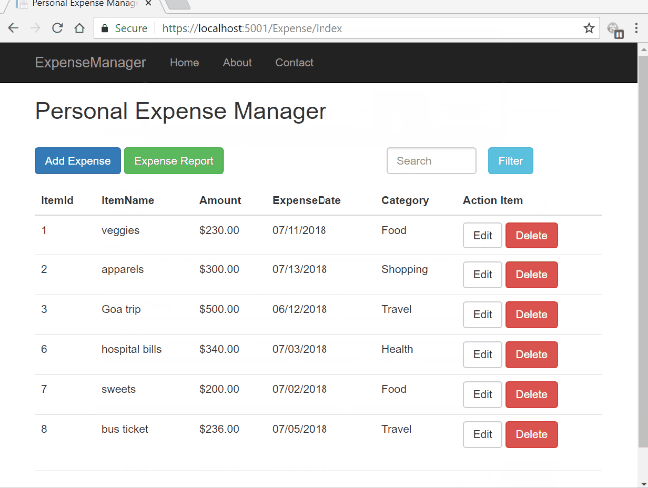
Prerequisites
- Install .NET Core 2.1 SDK from here
- Install the latest version of Visual Studio 2017 from here
- SQL Server 2008 or above
Source Code
Before proceeding, I would recommend you to get the source code from Github.
Create ASP.NET Core project
Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project.
After selecting the project, a “New Project” dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside Visual C# menu from the left panel.
Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from available project types. Put the name of the project as ExpenseManager and press OK to create the ASP.NET Core Project.

After clicking on OK, a new dialog will open asking to select the project template. You can observe two drop-down menus at the top left of the template window. Select “.NET Core” and “ASP.NET Core 2.1” from these dropdowns. Then, select “Web application (Model-View-Controller)” template and press OK.

Adding the Model to the Application
Since we are using Entity Framework Code first approach, so first we will create our model class and then generate our database tables using the model.
Right click on Models folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class
ExpenseReport.cs. This class will contain our Employee model properties.
Open
ExpenseReport.cs file and put in the following code into it.
We have used the [Key] attribute with
ItemId to consider it as the primary key while creating the database table.Creating the database table using EF Core code first approach
In order to create our tables using EF Core code first approach we need to install few nuget packages.
Navigate to Tools >> NuGet Package Manager >> Package Manager Console.
We have to install the package for the database provider that we are targeting which is SQL Server in this case. Hence, run the following command:
Since we are using Entity Framework Tools to create a table from the existing model, we will install the tools package as well. Hence, run the following command:
After the package installations are successful, we will create a dbcontext class. Add a file
ExpenseDBContext.cs in the Modals folder and put in the following code into it:
Do not forget to put your own connection string (inside ” “).
We will create a dataset migration which is used to keep the database schema in sync with the model. There is no database at this moment, so the first migration will create it and add tables for the entities represented by the DbSet properties on the ExpenseDBContext that we have created.
To create the dataset migration, navigate to the project folder and open the powershell window. Execute the following command in it.
Refer to the image below

This will create a folder named Migrations into our project, which contains the code for the migration and a model snapshot. Refer to the image below:

Enter the following command in the powershell window to execute the migration:
Refer to the image below:

This will create the table “ExpenseReport” in to our database that we have mentioned in the connection string. You can observe that the column
ItemId is the primary key here.
Hence, the database creation is completed successfully using Entity Framework code first approach.
Adding the Data Access layer to our application
Add a class file
ExpensesDataAcessLayer.cs into the Modals folder and put the following code in to it.
This file will have methods to handle CRUD operations on our database. We are also calculating the last six months expense and last four weeks expense for each category.
Adding the Controller to the Application
Right click on Controllers folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select “ASP.NET Core” from the left panel, then select “Controller class” from templates panel, and put the name as
ExpenseController.cs. Press OK.
This will create our controller ExpenseController inside Controllers folder. Open the
ExpenseController.cs file and put in the following code.
The controller will have the methods that will call our data access layer methods to handle database operations.
Adding Views to the Application
We will create three view files
- Index.cshtml: – this view will display all the expense data and contains a search box to search for a particular item.
- _expenseForm.cshtml: – this is a partial view, which contains the form to handle user inputs. This is used for both add and edit functionality and will be rendered in a modal dialog.
- _expenseReport.cshtml: – this is also a partial view, which will show the expense summary in a bar chart using Highcharts. It is also rendered as a modal dialog.
Index View
To create the view file, right click on the Index method in our controller and select “Add View…”. This will open an “Add MVC View” dialog box. Put in the name of view as Index and click Add. Make sure that “Create as a partial view” check box is not checked. Refer to image below:

This will create the
Index.cshtml file inside “Expense” folder under the Views folder. Open Index.cshtml file and put in the following code:
Let us understand this code. At the top we have included the bootstrap and jQuery references. After that we have added two buttons for adding a new expense and for creating the expense summary. We have also included a form containing a search box to filter out the records. On clicking of “Filter” button, the form is submitted and it invoked the Index method in our controller which will return the items matching the search criteria. The search functionality is provided only on item name field.
We are using a table to display all the expense records in our database and each record has two action button corresponding to it – Edit and Delete.
We have also created two modal dialog, one for adding/editing the expense data and another to display the expense summary report.
In the script section, we have defined
AddEditExpenses function. This function will be invoked when “Add Expense” or “Edit” button is clicked. We are passing the itemId as parameter in this method. If the “ItemId” value is not set then it is considered as Add function and if the “ItemId” is set then it is an Edit function. We will call “AddEditExpenses” in our controller which will return the partial view “_expenseForm” and bind it to ExpenseReport model. The modal will be empty for “Add” call and contain the expense item data in case of “Edit” call. Since we are using bootstrap datepicker to select the expense date, hence we have set the datepicker properties on modal dialog load.
The
ReportExpense function will call ExpenseSummary method in our controller, which will return the partial view “_expenseReport” to be displayed as a modal dialog. This partial view will display the monthly and weekly expense summary chart using Highcharts.
The
DeleteExpense function is used to delete the record of a particular expense. This will invoke the “Delete” method in our controller to remove the expense record from our database.
We are also using dynamic binding to bind the submit event of “expenseForm” modal. This form is defined in “_expenseForm.cshtml” view. On submitting of form, we are invoking an ajax call to the “Create” method in our controller class. Since we are using same form for both Edit and Add functionality so we need to distinguish among both using the ItemId value. In the “Create” method of controller, we will check if the ItemId is set then we will invoke
UpdateExpense method, else invoke AddExpense method. After successful submit, we will close the modal and redirect to Index view to show the updated list of expenses.ExpenseForm View
This is a partial view that will be displayed in a modal dialog on clicking of “Add Expense” button in Index view.
To create the view file, right click anywhere inside our controller file and select “Add View…”. This will open an “Add MVC View” dialog box. Put in the name of view as ““_expenseForm” and click Add. Make sure that “Create as a partial view” check box is selected. Refer to image below:

Open the “_expenseForm.cshtml file” and put in the following code in it
At the top, we are including the cdn reference to the bootstrap-datepicker so that we can use it in our modal dialog. Then we have a form element, which binds to our modal. We also have a submit button which will post the form data to the Create method in our controller using ajax call.
ExpenseReport View
This is a partial view that is displayed in the modal dialog on clicking “Expense Report” button in Index view. This view will display the expense report summary as bar graph with the help of Highcharts.
Create a new partial view ““_expenseReport.cshtml” and put in the following code in it.
On the top we have included the cdn reference to Highcharts. We have also provided two buttons to view monthly report of last six months and weekly report for last four weeks. The report will be generated as a bar chart to provide a comparative study of expense summary.
On click weekly report button, we will invoke the
GetWeeklyExpense method of our controller that will return the data in Json format and we will pass this to createCharts function to create the weekly expense bar chart using Highcharts.
Similarly, we will invoke
GetMonthlyExpense method of our controller on clicking of “Monthly Report” button and pass the Json result to createCharts function to create the monthly expense bar chart using Highcharts.Configure route URL
Open Startup.cs file to set the format for routing.Scroll down to app.UseMvc method, where you can set the route url.
Make sure that your route url is set like this
This url pattern sets ExpenseController as default controller and Index method as default action method. Default route parameters need not be present in the URL path for a match. If we do not append any controller name in the URL then it will take ExpenseController as default controller and Index method of ExpenseController as default action method. Similarly, if we append only “/Expense” to the URL, it will navigate to Index action method of Expense controller.
Execution Demo
Press F5 to launch the application. You can see a page similar to the one shown below.

Here we have “Add Expense” button to add a new expense report. The “Expense Report” button will open a dialog box to show the bar chart of monthly and weekly expense data. This bar chart is created with the hep of Highcharts. On the top right corner, we have a search box to search the records using item name.
Look at the below Gif image for the demo of application

Conclusion
We created a personal expense manager application using ASP.NET Core and Entity Framework Core with the help of Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2017. We have also used Highcharts to create a bar chart for monthly and weekly expense summary.
Please download the source code from GitHub and play around to get a better understanding.





0 comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.