In this article, I am going to discuss Exception Handling in C# with examples. This is one of the most important concepts in C#. As a developer, while developing an application, it is your key responsibility to handle the exception. The Exception Handling in C# is a procedure to handle the exception which occurred during the execution of a program. As part of this article, we are going to discuss the following pointers in details.
- What are the different types of errors?
- What is an Exception in C#?
- Who is responsible for abnormal termination of the program whenever runtime errors occur in the program?
- What happens if an exception is raised in the program?
- What CLR does when an exception occurred in the program?
- What is exception handling in C#?
- Why we need Exception Handling in C#?
- What is the procedure to Handle Exception in C#?
Types of errors in C#
When we write and execute our code in the .NET framework then there is a possibility of two types of error occurrences they are
- Compilation errors
- Runtime errors
Compilation Error in C#
An error that occurs in a program at the time of compilation is known as compilation error (compile-time error). These errors occur due to the syntactical mistakes under the program. That means these errors occur by typing the wrong syntax like missing double quotes and terminators, typing wrong spelling for keywords, assigning wrong data to a variable, trying to create an object for abstract class and interface, etc.
So in the simple word we can say that this type of error occurs due to the poor understanding of the programming language. These errors can be identified by the programmer and can be rectified before the execution of the program only. So these errors do not cause any harm to the program execution.
Runtime Error in C#
The errors which occurred at the time of program execution are called as the runtime error. These errors occurred when we entering wrong data into a variable, trying to open a file for which there is no permission, trying to connect to the database with wrong user id and password, the wrong implementation of logic, missing of required resources, etc.
Runtime errors are dangerous because whenever they occur in the program, the program terminates abnormally on the same line where the error gets occurred without executing the next line of code.
What is an Exception in C#?
A runtime error is known as an exception. The exception will cause the abnormal termination of the program execution. So these errors (exceptions) are very dangerous because whenever the exception occurs in the programs, the program gets terminated abnormally on the same line where the error gets occurred without executing the next line of code.
Who is responsible for abnormal termination of the program whenever runtime errors occur in the program?
Objects of exception classes are responsible for abnormal termination of the program whenever runtime errors (exceptions) occur. These exception classes are predefined under BCL (Base Class Libraries) where a separate class is provided for each and every different type of exception like
- IndexOutOfRangeException
- FormatException
- NullReferenceException
- DivideByZeroException
- FileNotFoundException
- SQLException,
- OverFlowException, etc.
Each exception class provides a specific exception error message. All the exception classes are responsible for abnormal termination of the program as well as after abnormal termination of the program they will be displaying an error message which specifies the reason for abnormal termination i.e. they provide an error message specific to that error.
So, whenever a runtime error (exception) occurs in a program, first the exception manager under the CLR (Common Language Runtime) identifies the type of error that occur in the program, then creates an object of the exception class related to that error and throws that object which will immediately terminate the program abnormally on the line where error got occur and display the error message related to that class.
What happens if an exception is raised in the program?
Program execution terminated abnormally. That means the statements placed after exception causing statement are not executed but the statements placed before that exception causing statement are executed by CLR.
What CLR does when an exception occurred in the program?
It creates the exception class object that is associated with that logical mistake and terminates the current method execution by throwing that exception object by using the “throw” keyword.
So we can say an exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of instruction execution. Let’s understand this with an example.
Example1: The below example shows program execution without exception
Output:

Example2: The below example shows program execution with the exception
OUTPUT:

After printing the above value it will give us the below error.

Explanation:
The CLR terminates the program execution by throwing DivideByZeroException because the logical mistake we committed here is dividing integer number by integer zero. As we know it is not possible to divide an integer number by zero.
From the above program, we can define the exception technically as
- An exception is an event because when an exception is raised CLR internally executes some logic to prepare that exception related messages.
- The Exception is a signal because by looking into exception message developer will take necessary actions against that exception.
- An exception is an object because for throwing exception CLR or we should create an appropriate class object.
Is the above exception message is user understandable?
Definitely, the answer is no, the user cannot understand the above exception message because they are .NET based exception messages. So the user cannot take any decision alone to resolve the above problem. A developer should guide to solve the above problem.
What is the solution for the above problem?
It is the developer’s responsibility to convert .NET exception messages into user understandable message format. To solve this problem developer should the exception handling in C#. Using exception handling code, the developer can catch the exception and can print and pass user understandable messages.
What is exception handling in C#?
The process of catching the exception for converting the CLR given exception message to end-user understandable message or for stopping the abnormal termination of the program whenever runtime errors are occurring is called Exception Handling in C#.
Once we handle an exception under a program we will be getting following advantages
- We can stop the abnormal termination
- We can perform any corrective action that may resolve the problem occurring due to abnormal termination.
- Displaying a user-friendly error message, so that the client can resolve the problem provided if it is under his control.
Why we need Exception Handling in C#?
We need Exception Handling in C# because
- To stop the abnormal termination of the program
- To provide user understandable messages when an exception is raised. So that users can make a decision without the developer’s help.
Basically, by implementing Exception handling we are providing life to a program to talk to the user on behalf of a developer.
What is the procedure to Handle Exception in C#?
The Exception Handling in C# is a 4 steps procedure
- Preparing the exception object appropriate to the current logical mistake.
- Throwing that exception to the appropriate exception handler.
- Catching that exception
- Taking necessary actions against that exception
How can we handle an exception in .NET?
There are three methods to handle the exception in .NET
- Logical implementation
- Try catch implementation
- On error go to implementation
What is logical implementation?
In this method, we handle the exception by using logical statements. In real-time programming, the first and foremost importance always given to logical implementation only. If it is not possible to handle an exception using logical implementation then we use try-catch implementation.
Example3: Handling exception using logical implementation
OUTPUT:

In the above example when the user entered the second number as zero exception will be raised and that is handled using logical implementation.
But while we are entering two numbers instead of the number if we entered any character then it will give you one exception that is FormatException which is not handled in this program.

Here we entered the second value as abc. So it will give us the below exception.

So to handle such type of exception we need to go for Try catch implementation.
Exception handling in C# using the Try Catch implementation
To implement the try-catch implementation .NET framework provides three keywords
- Try
- Catch
- finally
try:
The try keyword establishes a block in which we need to write the exception causing and its related statements. That means exception causing statements must be placed in the try block so that we can handle and catch that exception for stopping abnormal termination and to display end-user understandable messages.
Catch:
The catch block is used to catch the exception that is thrown from its corresponding try block. It has the logic to take necessary actions on that caught exception.
Catch block syntax is look like a constructor. It does not take accessibility modifier, normal modifier, return type. It takes the only single parameter of type Exception.
Inside catch block, we can write any statement which is legal in .NET including raising an exception.
Finally:
The keyword finally establishes a block that definitely executes statements placed in it.
Statements that are placed in finally block are always executed irrespective of the way the control is coming out from the try block either by completing normally or throwing an exception by catching or not catching.
Syntax to use Exception Handling:

Once we use the try and catch blocks in our code the execution takes place as following
- If all the statements under try block are executed successfully, from the last statement of the try block, the control directly jumps to the first statement that is present after the catch block (after all catch blocks) without executing catch block (it means there is no runtime error in the code at all ).
- Then if any of the statements in the try block causes an error, from that statement without executing any other statements in the try block, the control directly jumps to the catch blocks searching for a catch block to handle that exception.
- If a proper catch block is available that handles the exception, then the abnormal termination stops there, executes the code under the catch block and from there again it jumps to the first statement after all the catch blocks.
- Then if a matching catch is not available abnormal termination occurs again.
Example4: Program to handle an exception using try-catch implementation with the generic catch
Note: catch block without exception class is called a generic catch and this catch block can handle any type of exception that is raised in the corresponding try block.
OUTPUT1: Enter the value as 10 and 0
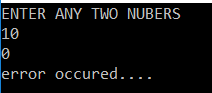
OUTPUT2: Enter the value as 10 and abc
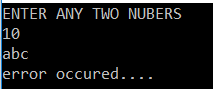
In the above example, there is no exception class used in the try block, so it is known as the generic catch block.
The problem with the generic catch block is that, any kind of exception may occur the same message will be displayed to the user and the user cannot understand why the error has occurred; to overcome this, specific catch blocks are used.
Using specific catch blocks it is possible to know more information about the exception.
What are the properties of Exception Class in C#?
The C# exception class has 3 properties are as follows
- Message: This property will store the reason why an exception has occurred.
- Source: This property will store the name of the application from which exception has been raised.
- Help link: This is used to provide a link to any file /URL to give helpful information to the user when an exception is raised.
Example5: Program to handle an exception using try-catch implementation with the specific catch
OUTPUT:
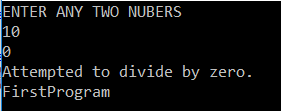
In the above example, the superclass exception is used to handle the exception. But if we use the super Exception class when there is any relevant class is available, it will kill the execution performance of the program.
In the next article, I will discuss how to use multiple catch blocks and finally block in C#. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Exception handling in C# step by step with some examples. I hope you understood how to implement Exception Handling in C#.





0 comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.