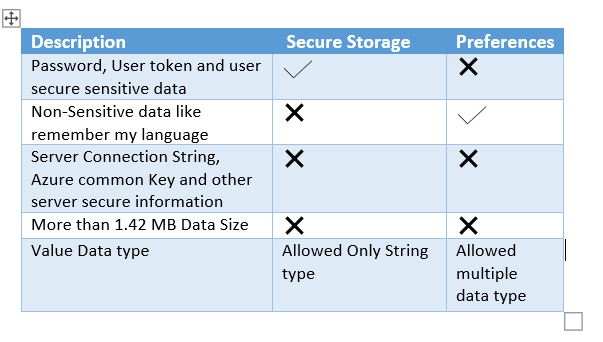
In this Ionic 5/4 tutorial, we’ll learn how to show Alerts, Confirm and Prompt message overlays in an Ionic application by using the AlertController available in UI components of Ionic Framework.
What are Alerts?
To quickly draw the attention of a user, we generally show an Alert message which can display a text message or allow a user to select an option. An Alert is shown over the content of the page which can be closed only by some user actions.
In Ionic, we can create Alerts or Confirm overlays by using the AlertController class provided by Ionic Framework UI components.
Here we will learn three types of Alerts that can be easily implemented and used for different purposes:
Alert messages with an OK button.
Confirm alerts of taking and input from users. Mainly used to Delete actions where we confirm if the user really wants to delete.
Prompt message which will take date inputs from user and display on the page. We’ll also learn how to customize the CSS style of Ionic Alert UI components.
Let’s start the implementation…
Install or Update Ionic CLI
To create Ionic applications, you need to install @ionic/cli package. If already have updated it to the latest version
$ npm install -g @ionic/cliCreate new Ionic Angular Application
We’ll create a new Ionic 5 application using Angular framework with a starter blank template.
$ ionic start ionic-alert-app blank --type=angularThe --type option property is used to select the framework we want to use for our Ionic application Move to the application directory
$ cd ionic-alert-app
Now you can run the Ionic application by hitting
$ ionic serve --labThe--lab option is used to open the application in the browser into a lab viewer where you can concurrently see how it will look on multiple platforms including Android, iOS, and Windows.
Implementing Alerts in Page
To create Alerts, we need to import the AlertController class from '@ionic/angular' then add in the class constructor() method to use its functions.
// home.page.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { AlertController } from '@ionic/angular';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
})
export class HomePage {
constructor(
public alertController: AlertController
) { }
....
....
}
The AlertController provides three methods:
create(): It is used to create a new Alert component instance and returns a promise. The create method takes option properties for the Alert component.dismiss(): This is used to close the visible Alert message programmatically by using the instance of create() method.
getTop(): This method fetches the ID of the opened Alert component so that we can close using the dismiss() method.
Showing Alert Message
The create() method is used to create an Alert component, which is then shown by calling present()
showAlert() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Alert',
subHeader: 'Subtitle for alert',
message: 'This is an alert message.',
buttons: ['OK']
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}We used promise above, but async;await can also be used to deal with methods who returns a promise in the following way:
async showAlert() {
const alert = await this.alertController.create({
header: 'Alert',
subHeader: 'Subtitle for alert',
message: 'This is an alert message.',
buttons: ['OK']
});
await alert.present();
}The create() method takes option properties to define Title, message, and buttons to show for action.
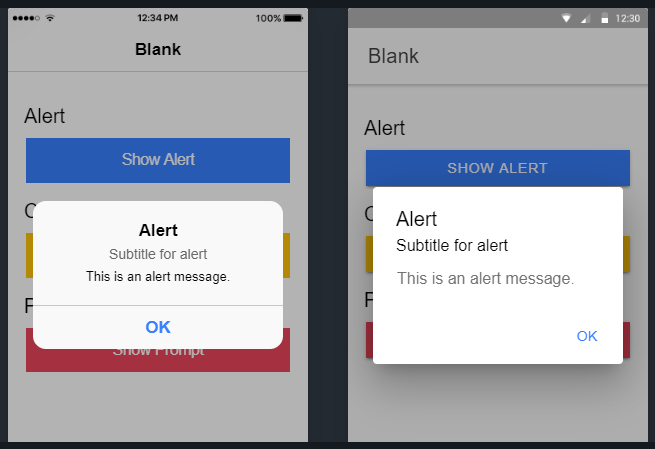
Show Confirm Alert
A confirm Alert is different as it can take multiple action inputs from the user through action buttons.
showConfirm() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Confirm Alert',
subHeader: 'Beware lets confirm',
message: 'Are you sure? you want to leave without safty mask?',
buttons: [
{
text: 'Never',
handler: () => {
console.log('I care about humanity');
}
},
{
text: 'Not Sure',
handler: () => {
console.log('Let me think');
}
},
{
text: 'Yes!',
handler: () => {
console.log('Whatever');
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}We can define any number of action buttons in the buttons property array with their own handler callback.
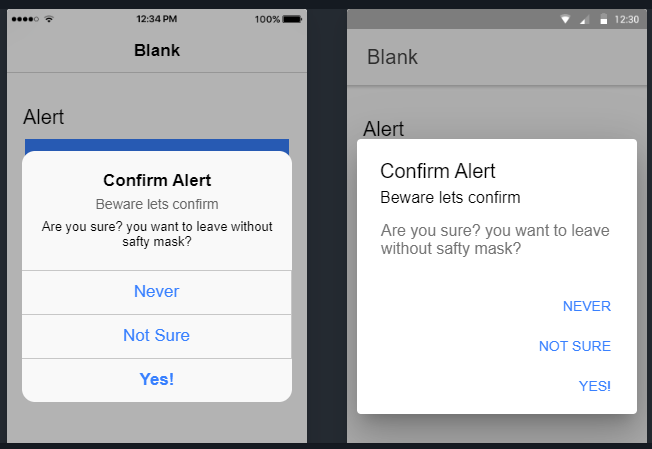
Show a Prompt Alert
The default Ionic Prompt Alert can be created to take a textual value from uses in a textbox control by adding below method:
showPrompt() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Prompt Alert',
subHeader: 'Enter information requested',
message: 'Enter your favorate place',
inputs: [
{
name: 'Place',
placeholder: 'Eg.NY',
},
],
buttons: [
{
text: 'Cancel',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Canceled', data);
}
},
{
text: 'Done!',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Saved Information', data);
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
Types of Form Controls in Prompt Alert
A property alert can take any type of information using form controls types including ‘date‘, ‘email‘, ‘number‘, ‘password‘, ‘search‘, ‘tel‘, ‘text‘, ‘url‘, ‘time‘
Properties For Each Form Control
The inputs property takes an array of form control types with the following properties:
type: Type of form controlname: Define the name of the form control.placeholder: Define placeholder of the form control.value: Define the default value of the form control.label: Define the label of the form control.checked: Used for Checkbox or Radio control.disabled: Control disabled state.id: Specific ID for control.handler: Bind a handler callback for each control.min: Set min value.max: Set max value.cssClass: Adds a custom CSS class.
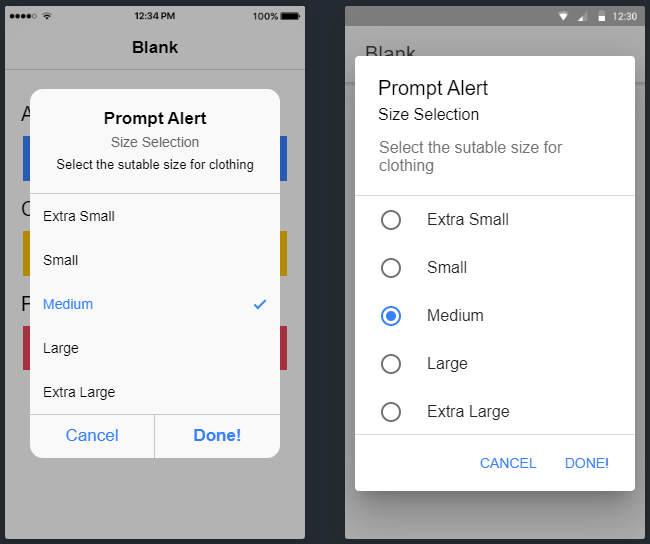
Prompt Alert with Radio List
Prompt alert with a list of Radio controls to choose a value.
showPrompt() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Prompt Alert',
subHeader: 'Size Selection',
message: 'Select the sutable size for clothing',
inputs: [
{
type: 'radio',
label: 'Extra Small',
value: 'xs'
},
{
type: 'radio',
label: 'Small',
value: 's'
},
{
type: 'radio',
label: 'Medium',
value: 'm'
},
{
type: 'radio',
label: 'Large',
value: 'l'
},
{
type: 'radio',
label: 'Extra Large',
value: 'xl'
}
],
buttons: [
{
text: 'Cancel',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Canceled', data);
}
},
{
text: 'Done!',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Selected Information', data);
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
Prompt Alert with Checkbox List
Similarly, we can add a list of Checkboxes to select single or multiple values available
showPrompt() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Prompt Alert',
subHeader: 'Member Selection',
message: 'Select family members',
inputs: [
{
type: 'checkbox',
label: 'Self',
value: 'self',
checked: true,
disabled: true
},
{
type: 'checkbox',
label: 'Mother',
value: 'mother'
},
{
type: 'checkbox',
label: 'Father',
value: 'father'
},
{
type: 'checkbox',
label: 'Son',
value: 'son'
},
{
type: 'checkbox',
label: 'Daughter',
value: 'daughter'
}
],
buttons: [
{
text: 'Cancel',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Canceled', data);
}
},
{
text: 'Done!',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Selected Information', data);
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
Customize CSS Style of Alert Component
The cssClass property takes a class name that can be added to the Alert overlay modal, using which we can easily customize the style.
async showAlert() {
const alert = await this.alertController.create({
header: 'Alert',
cssClass:'my-custom-class',
subHeader: 'Subtitle for alert',
message: 'This is an alert message.',
buttons: ['OK']
});
await alert.present();
}Now add the custom style to global.scss file at application root.
.my-custom-class {
--backdrop-opacity: 0.2;
--background: linear-gradient(90deg, rgba(165, 255, 192, 1) 1%, rgba(0, 212, 255, 1) 100%);
}
Following CSS properties are available:
--backdrop-opacity: Opacity of the backdrop--background: Background of the alert--height: Height of the alert--max-height: Maximum height of the alert--max-width: Maximum width of the alert--min-height: Minimum height of the alert--min-width: Minimum width of the alert--width: Width of the alert
Update Home Template
In the Home template, we have three buttons to call the methods we discussed above.
<ion-header [translucent]="true">
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>
Ionic Alerts
</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content [fullscreen]="true" class="ion-padding">
<h4>Alert</h4>
<ion-button color="primary" expand="full" (click)="showAlert()">Show Alert</ion-button>
<h4>Confirm</h4>
<ion-button color="warning" expand="full" (click)="showConfirm()">Show Confirm</ion-button>
<h4>Prompt</h4>
<ion-button color="danger" expand="full" (click)="showPrompt()">Show Prompt</ion-button> <code>{{selectedData | json }}</code>
</ion-content>
Final Component Class
After adding all methods the home.page.ts file will look like this:
// home.page.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { AlertController } from '@ionic/angular';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
})
export class HomePage {
selectedData: any;
constructor(
public alertController: AlertController
) { }
showAlert() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Alert',
subHeader: 'Subtitle for alert',
message: 'This is an alert message.',
buttons: ['OK']
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
showConfirm() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Confirm Alert',
subHeader: 'Beware lets confirm',
message: 'Are you sure? you want to leave without safty mask?',
buttons: [
{
text: 'Never',
handler: () => {
console.log('I care about humanity');
}
},
{
text: 'Not Sure',
handler: () => {
console.log('Let me think');
}
},
{
text: 'Yes!',
handler: () => {
console.log('Whatever');
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
showPrompt() {
this.alertController.create({
header: 'Prompt Alert',
subHeader: 'Enter information requested',
message: 'Enter your favorate place',
inputs: [
{
name: 'Place',
placeholder: 'Eg.NY',
},
],
buttons: [
{
text: 'Cancel',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Canceled', data);
}
},
{
text: 'Done!',
handler: (data: any) => {
console.log('Saved Information', data);
this.selectedData = data;
}
}
]
}).then(res => {
res.present();
});
}
}
Source Code
Find source code in my GitHub repository here.
Conclusion
Finally, we are done with Ionic Alerts tutorial, We discussed how to add Alerts, Confirm Alerts and Prompt Alerts in the Ionic application by using the methods available in AlertController class. We can easily customize the Alert box and have multiple form controls as well in prompt type alerts.
Hope this was helpful, do share your comments and feedback.
Thanks for reading…